Spinal Fusion Surgery: A Proven Solution for Spinal Instability
Presented by cckaam
What Is Spinal Fusion?
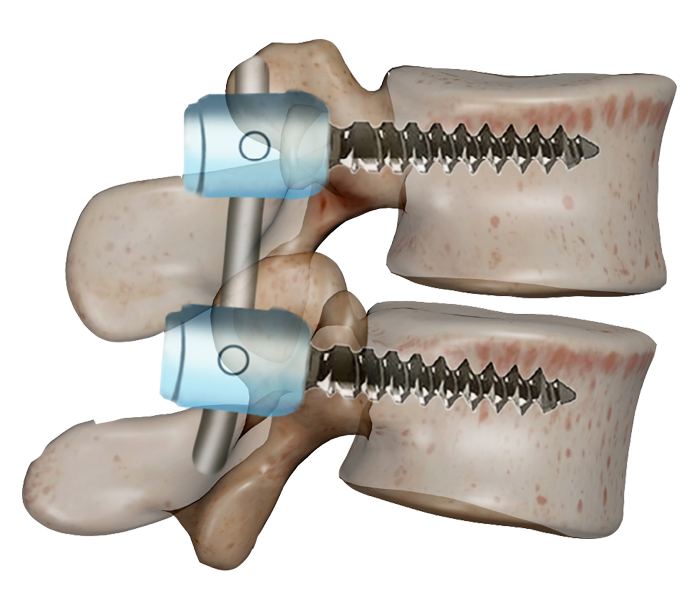
Spinal Fusion is an advanced surgical procedure in the fields of orthopedics and neurosurgery, aimed at stabilizing specific segments of the spine. In this operation, two or more vertebrae are permanently joined using screws, rods, plates, or bone grafts, gradually forming a single solid bone unit over time.
The primary goals of this surgery are to reduce chronic pain, correct spinal deformities or instability, and prevent abnormal vertebral movement that may compress the spinal cord or nerve roots.
Which Conditions Are Treated with Spinal Fusion?
Spinal Fusion is commonly recommended for the following spinal disorders:
- Spondylolisthesis
A condition where one vertebra slips forward over the one beneath it, leading to instability and pain. Spinal Fusion stabilizes the vertebrae, halting the progression and relieving symptoms.
- Scoliosis and Kyphosis
In structural deformities like scoliosis (lateral curvature) or kyphosis (hunchback), spinal fusion straightens and restores the natural alignment of the spine.
- Degenerative Disc Disease
Worn-out or damaged intervertebral discs can lead to painful and unstable spinal segments. Fusion eliminates excessive motion and provides lasting pain relief.
- Recurrent or Chronic Herniated Discs
When disc herniation recurs or fails to respond to non-surgical treatments, spinal fusion becomes a definitive solution to prevent further nerve compression.
- Spinal Fractures
Traumatic injuries such as falls or accidents can result in fractured vertebrae. Fusion stabilizes these segments and protects the spinal cord from further damage.
- Spinal Infections or Tumors
In cases of vertebral infections (osteomyelitis) or tumors, spinal fusion reinforces structural integrity following removal or treatment of the affected area.
The Spinal Fusion Procedure: Step by Step
- Preoperative Preparation
- Comprehensive physical examination
- Diagnostic imaging (MRI, CT scan, or X-rays)
- Necessary blood and lab tests
- Anesthesia and Surgical Approach
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Depending on the location of the problem, the surgeon may approach the spine from the front (anterior), back (posterior), or side (lateral).
- Fusion Technique
- Insertion of screws and rods to stabilize the vertebrae
- Placement of bone grafts (autografts from the patient’s pelvis or synthetic/biological alternatives)
- In some cases, removal of the intervertebral disc and replacement with bone material
- Postoperative Care
The surgical site is closed, and the patient is closely monitored in a recovery unit. After discharge, pain management, physical therapy, and sometimes a spinal brace are prescribed to aid healing.
Recovery Timeline
- Hospital Stay: Typically 3 to 5 days
- Return to Daily Activities: 4 to 8 weeks
- Complete Bone Fusion: 3 to 6 months
Following the surgeon’s instructions regarding physical activity, rehabilitation, and posture limitations is essential to avoid complications and ensure successful healing.
Is Spinal Fusion Effective?
In the majority of cases, Spinal Fusion significantly reduces pain, improves mobility, and enhances the patient’s quality of life. Clinical studies report a success rate of over 90%, depending on the patient’s condition, underlying diagnosis, and the surgical technique used.
Final Thoughts
Spinal Fusion is considered one of the most effective surgical solutions for complex spinal disorders. It not only relieves disabling back pain but also restores spinal stability and improves overall body function. Choosing a reputable medical center and an experienced spinal surgeon is vital to the success of this procedure.
If you’re experiencing spinal instability or chronic back pain and want to explore your treatment options, scheduling a consultation with a specialist in spinal surgery is the most important first step.
cckaam is here to guide you through your spine care journey—connecting you to Iran’s top hospitals, expert surgeons, and personalized treatment programs.