Knee Replacement Surgery: A Proven Solution for Chronic Pain and Limited Mobility
Introduction
The knee is one of the most complex and essential joints in the human body, playing a critical role in mobility, balance, and weight-bearing. Over time, due to aging, injury, or medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or sports-related trauma, the knee joint may become worn down or damaged, leading to chronic pain and reduced function. When non-surgical treatments no longer provide relief, knee replacement surgery is considered one of the most effective solutions.
What Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
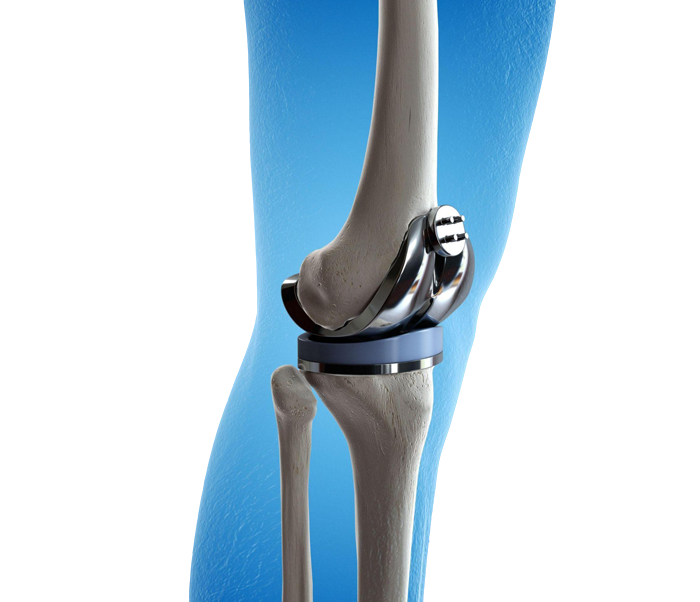
Knee replacement surgery (Total or Partial Knee Arthroplasty) involves replacing the damaged or worn-out parts of the knee joint with artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or polyethylene. The goal is to relieve pain, restore natural movement, correct deformities, and significantly enhance the patient’s quality of life.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
All three components of the knee—femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and sometimes the patella (kneecap)—are replaced with prosthetic implants. - Partial Knee Replacement (Unicompartmental):
If damage is confined to a single compartment of the knee (medial or lateral), only that portion is replaced. This is a less invasive option with a faster recovery. - Simultaneous Bilateral Knee Replacement:
In cases where both knees are severely affected, both joints can be replaced during one surgical session, depending on the patient’s overall health and medical condition.
When Is Knee Replacement Needed?
You may be a candidate for surgery if you experience:
• Persistent, medication-resistant knee pain
• Difficulty performing everyday activities such as walking or climbing stairs
• Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning
• Grinding or clicking sounds during movement
• Visible knee deformities (bow-legged or knock-kneed appearance)
• Significant loss of mobility and quality of life
Treatment Process: Step by Step
- Preoperative Evaluation:
The orthopedic surgeon conducts a thorough clinical exam, blood tests, imaging (X-ray, MRI), and consults with cardiologists and anesthesiologists to ensure the patient is fit for surgery. - Surgery:
Performed under general or spinal anesthesia, the procedure typically takes 1–2 hours. Damaged bone surfaces are carefully removed and replaced with prosthetics using either cemented or cementless fixation techniques. - Recovery & Rehabilitation:
- Hospital Stay: 2 to 4 days
- Physical therapy starts the day after surgery
- Return to light activities: Around 6 weeks post-op
- Full recovery: 3 to 6 months after surgery
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
✓ Long-term relief from chronic joint pain
✓ Improved range of motion and flexibility
✓ Restoration of independence in daily activities
✓ Boost in confidence and mental well-being
✓ Correction of deformities and improved leg alignment
✓ Enhanced social, professional, and physical engagement
Potential Challenges and Risks
While highly successful, like any major surgery, knee replacement can come with potential risks:
• Postoperative infections (manageable with antibiotics)
• Blood clots in the legs or lungs (preventable with early mobilization and medication)
• Joint stiffness or reduced mobility
• Prosthesis loosening or wear over time
• Possible need for revision surgery after 15–20 years
• Rare allergic reactions to implant materials
Latest Advances in Knee Replacement
- Robotic-assisted surgery and 3D imaging for enhanced precision
• Next-generation prosthetics with improved durability
• Minimally invasive techniques for quicker recovery and smaller incisions
• Custom-fitted implants tailored to each patient’s anatomy
Who Is a Good Candidate for Knee Replacement?
This surgery is most commonly performed on individuals aged 50 to 80. However, it may also be appropriate for younger or older patients in special cases, especially when:
• Severe pain interferes with daily life
• Other treatments have failed
• The joint is deformed or severely deteriorated
• Mobility has significantly decreased
Conclusion
Knee replacement is one of the most successful and widely performed orthopedic surgeries of the modern era. It not only alleviates pain and restores mobility but also drastically improves overall quality of life. While the recovery period and potential risks should be considered, choosing the right surgeon, a well-equipped hospital, and strictly following postoperative care instructions ensures a highly satisfying outcome.
Through CCKAAM, patients from around the world can access world-class orthopedic care in Iran with full support at every stage—from planning and surgery to rehabilitation and recovery.