Tissue Expander Treatment: An Advanced Approach to Tissue Repair and Reconstruction
Introduction
In reconstructive surgery, one of the main challenges surgeons face is the restoration and repair of lost or damaged tissue. Tissue Expander is a modern and effective technique that allows surgeons to stretch and expand tissues such as skin, muscles, and other tissues for further repair and reconstruction. This method is particularly used in aesthetic and reconstructive surgeries, including post-burn, cancer, and trauma surgeries. This article thoroughly examines the Tissue Expander method, its advantages, stages, applications, and key considerations.
What is a Tissue Expander?
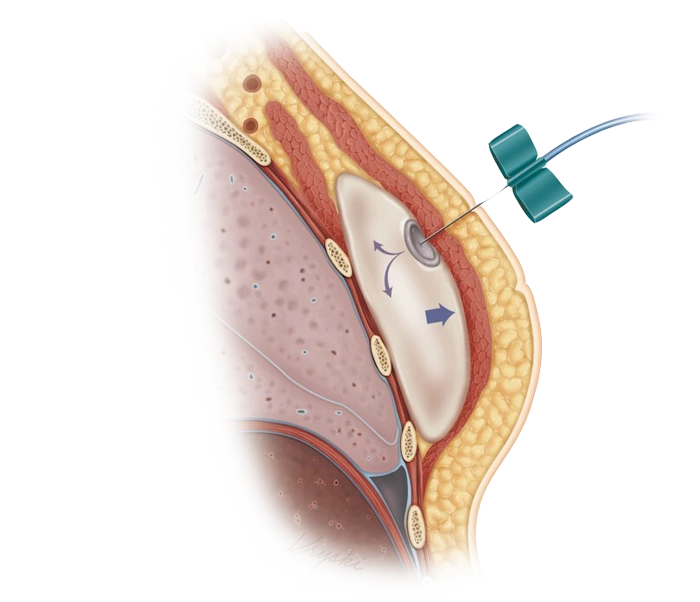
A Tissue Expander is a device that allows surgeons to gradually stretch specific tissues of the body, such as the skin, to make them more suitable for subsequent reconstructive surgeries or grafts. This device is usually a silicone bag placed beneath the skin, which is gradually filled with liquid or air. This process causes the skin and surrounding tissues to stretch, creating the necessary space for reconstructive or graft surgeries.
Applications of Tissue Expander
Tissue Expanders are used in various types of reconstructive and cosmetic surgeries, including:
- Post-Burn Surgery: In these surgeries, damaged skin is stretched using a Tissue Expander to replace lost sections of skin.
- Cancer Surgery: Patients with cancers such as breast cancer may need to reconstruct skin or other tissues after the removal of cancerous tissues. Tissue Expanders are used in this process.
- Reconstructive Surgery Post-Accidents and Injuries: In cases where tissues are damaged due to accidents or injuries, Tissue Expanders assist in repairing and reconstructing these tissues.
- Cosmetic Surgery: In certain cosmetic surgeries, this technique is employed to improve the appearance and shape of the body.
How Does a Tissue Expander Work?
The process of using a Tissue Expander generally involves the following steps:
- Placing the Tissue Expander Beneath the Skin: Initially, the surgeon creates a small incision in the affected area to place the Tissue Expander beneath the skin. This device is typically placed in areas that require additional stretching.
- Filling the Tissue Expander: Once in position, the surgeon gradually fills the Tissue Expander with air or a saline solution using a syringe. This step initiates the tissue stretching process.
- Gradual Process Over Time: The Tissue Expander is gradually filled over specific time intervals. This process may take several weeks to months to sufficiently stretch the skin and prepare it for future surgeries.
- Final Reconstructive Surgery: After the tissues are sufficiently stretched, the Tissue Expander is removed, and the surgeon performs the final reconstruction using the newly created tissue or a graft.
Advantages of Treatment Using Tissue Expander
This method is highly effective in reconstructive surgeries for several reasons:
- No Need for Direct Grafts: In many cases, the need for skin or tissue grafts from other parts of the body is reduced since the existing tissues are stretched enough for reconstructive surgery.
- More Natural Results: Because the patient’s own tissues are used for repair, the results are more natural, and the risk of graft rejection is minimized.
- Minimal Side Effects: Compared to other reconstructive methods, the use of Tissue Expanders has the least risks and side effects.
- Gradual Healing Process: Due to the gradual nature of the tissue stretching process, the surgical outcomes are achieved over time with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Steps in Tissue Expander Treatment
- Initial Consultation: Before beginning treatment, the patient must consult with a specialized doctor to determine if a Tissue Expander is the appropriate option. The doctor may perform various tests to ensure the patient’s overall health and the suitability of the method.
- Initial Surgery: After preparing the treatment area, the surgeon places the Tissue Expander beneath the skin. This surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia.
- Gradual Expansion: Over the course of several weeks, the patient needs to visit regularly to have the Tissue Expander filled, gradually stretching the tissues.
- Final Surgery: Once the skin is sufficiently stretched, the Tissue Expander is removed, and the final reconstruction or tissue grafting is performed.
- Post-Operative Care: After the final surgery, the patient requires post-operative care to prevent complications and ensure a smooth recovery process.
Complications and Important Considerations
While the use of Tissue Expanders is generally safe and effective, like any medical procedure, some side effects may occur:
- Infection: There may be an infection at the site of the Tissue Expander placement, which requires immediate treatment.
- Pain and Discomfort: The patient may experience pain and discomfort during the tissue expansion process.
- Bleeding: In some cases, mild bleeding may occur.
- Expansion Issues: Occasionally, the tissue expansion process may encounter difficulties that require consultation with the doctor.
Conclusion
The use of Tissue Expanders is an innovative and effective method in reconstructive surgery that allows for the rebuilding of damaged or lost tissues. With its numerous advantages, including more natural results and reduced need for skin grafts, it has become one of the best options for patients seeking reconstructive treatments. Along with this, having proper consultation and post-operative care is essential to achieving the best possible results.
Given the advancements in medical technology, Tissue Expanders are recognized as a reliable and proven solution in the field of reconstructive surgery, significantly improving the quality of life for patients.