Skin Cancer: All About Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatments
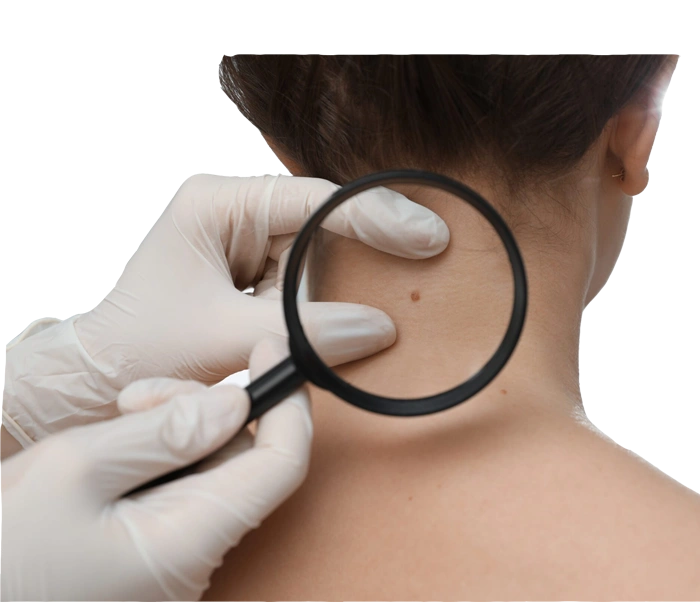
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, often resulting from uncontrollable skin cell growth. It typically appears in areas of the skin most exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, hands, and back. Since most skin cancers are directly caused by ultraviolet (UV) light or similar radiation, individuals living in tropical areas or who spend long hours in the sun are at higher risk.
Types of Skin Cancer
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- The most common type of skin cancer, it usually appears in sun-exposed areas like the face and neck. BCC generally grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
- Symptoms: Small, bleeding sores or lumps that do not heal.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- This type of skin cancer typically occurs in areas of the skin most damaged by the sun, such as the face, hands, and ears. SCC grows faster than BCC but typically does not spread to other organs.
- Symptoms: Red, raised lumps or non-healing sores that bleed easily.
- Melanoma
- Melanoma is one of the most dangerous types of skin cancer, originating from melanocytes (skin pigment-producing cells). It can spread quickly to other parts of the body.
- Symptoms: Changes in the size or color of moles or the appearance of new moles, especially those with irregular borders or uneven coloring.
Causes and Risk Factors of Skin Cancer
- Sunlight and UV Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a major cause of skin cancer. This radiation comes in two forms: UVA and UVB, both of which can damage skin DNA and cause cancer. Prolonged and unprotected sun exposure, especially in childhood and adolescence, increases the risk of developing skin cancer. - Family History
Individuals with a family history of skin cancer are at higher risk. - Fair Skin
People with fair skin, light eyes, and blonde or red hair are more sensitive to UV rays and at a greater risk. - High Number of Moles or Skin Spots
Those with numerous moles or irregularly shaped or large moles are at greater risk. - Smoking
Smoking can increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma. - Tanning Beds and Sunlamps
Artificial tanning devices can increase the risk of skin cancer.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
- Changes in Existing Moles or Skin Spots
Alterations in size, shape, or color of existing moles can indicate skin cancer. - Appearance of New Growths
New lumps or sores on the skin that bleed and do not heal may signal skin cancer. - Persistent Sores
Sores that continuously bleed or don’t heal. - Itching or Pain
Skin cancer can sometimes cause itching or pain in the affected area.
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer
- Physical Examination
The doctor will thoroughly examine your skin to identify any unusual changes. - Skin Biopsy
If the doctor suspects cancer, a biopsy is performed to take a sample of the tissue for further examination. - Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests may be conducted to check for cancer spread.
Skin Cancer Treatment
Treatment depends on the cancer’s type and severity, often including:
- Surgery
The most common and effective treatment method for skin cancer. It may involve removing the tumor entirely or using microsurgery for precision removal of cancerous cells. - Radiation Therapy
High-energy radiation is used to destroy cancer cells, typically for cancers in hard-to-reach areas. - Immunotherapy
Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer, mainly used for melanoma. - Chemotherapy
Often used when skin cancer has spread beyond the skin, chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. - Topical Treatments
For early-stage skin cancer, topical treatments like 5-FU cream can be used.
Proper Nutrition for Skin Cancer Patients
A healthy diet is crucial for cancer patients, as it helps strengthen the immune system and manage side effects from treatments.
- Beneficial Foods:
Dark leafy greens (e.g., spinach, broccoli), antioxidant-rich fruits (e.g., blueberries, pomegranates), fatty fish (e.g., salmon), nuts, seeds (e.g., walnuts, chia seeds), whole grains, and green tea. - Foods to Limit:
Processed meats, fried foods, sugary items, and alcohol.
The Role of a Psychologist in Skin Cancer Treatment
Skin cancer impacts not only the body but also the mind. Concerns about appearance, anxiety due to illness, and stress from treatments can interfere with recovery. Therefore, a psychologist can help manage mental health alongside physical treatment.
Psychological services include individual counseling before and after treatment, stress reduction techniques, and family support sessions.