Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of One of the Most Common Cancers in Women
Introduction
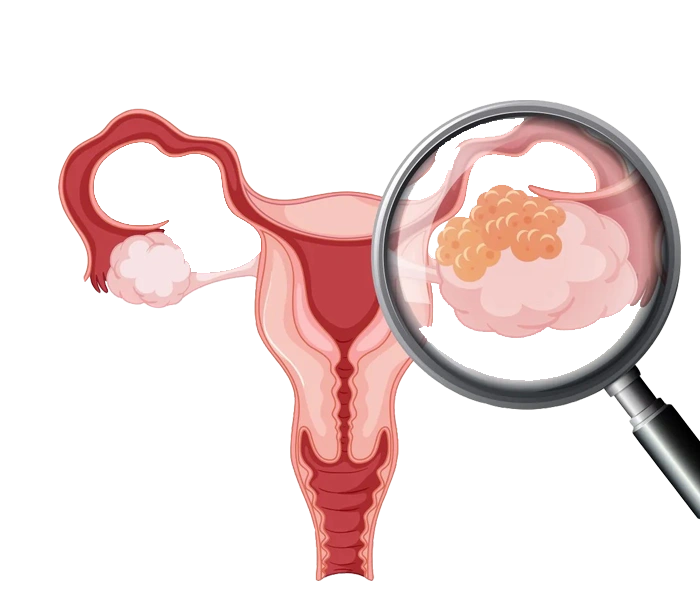
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries. This cancer usually has no symptoms in the early stages, which is why it is often diagnosed at more advanced stages. Ovarian cancer has garnered particular attention from oncologists due to the variety of treatment options available, which can significantly impact the survival and quality of life of patients. This article explores various aspects of ovarian cancer, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.
What is the Ovarian System?
The ovaries are one of the main organs of the female reproductive system, playing a crucial role in producing eggs as well as hormones like estrogen and progesterone. They are an essential part of the female reproductive system, directly linked to fertility and menstruation. Any disruption in ovarian function can lead to several health problems, one of which is ovarian cancer.
Definition of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the ovaries and can spread to other parts of the body. There are two main types of ovarian cancer: epithelial ovarian cancer (the most common type) and other types such as sarcomas and germ cell tumors. Ovarian cancer typically shows no specific symptoms in its early stages, which is why it is often diagnosed when the disease is already advanced.
Incidence and Epidemiology
- Prevalence: Ovarian cancer is one of the most common cancers in women, particularly affecting women over the age of 50.
- Age: Two age peaks are observed for the onset of ovarian cancer: one between 40 and 60 years, and another after menopause.
- Gender: Ovarian cancer only occurs in women.
- Geography: The incidence of this cancer is higher in developed countries compared to developing ones.
Causes and Risk Factors
Although the exact cause of ovarian cancer is not yet fully understood, several factors increase the risk of developing this disease:
- Family History: Women with a family history of ovarian cancer or other cancers of the reproductive system are at higher risk.
- Age Over 50: Aging is a significant risk factor for ovarian cancer.
- Hormones: Long-term use of hormone therapy, such as postmenopausal hormone treatments, can increase the risk.
- Reproductive History: Women who have never been pregnant or have had children later in life (after age 35) are at higher risk.
Clinical Symptoms
Symptoms of ovarian cancer may be mild and unclear in its early stages. However, the most common symptoms include:
- Abdominal and Pelvic Pain: There may be discomfort or a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen or pelvic area.
- Bloating and Increased Abdominal Size: Bloating and changes in the shape of the abdomen, which may worsen over time.
- Changes in Urinary Patterns: Increased or decreased frequency of urination and the feeling of bladder fullness.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Weight loss without a clear reason.
- Digestive Problems: Issues like constipation and difficulty in digestion.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
To diagnose ovarian cancer, doctors use a variety of methods, including:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough examination of the abdomen and pelvis to identify any masses or changes in the ovaries’ size.
- Imaging Tests: These include ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs to view tumors and determine the cancer’s stage.
- Blood Tests: Measuring tumor markers such as CA-125, which can help in diagnosing ovarian cancer.
- Biopsy: In some cases, doctors may take a sample from suspicious masses to examine cancer cells.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
The treatment for ovarian cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment methods include:
- Surgery: The most common treatment method, which involves removing the ovaries and tumors.
- Chemotherapy: The use of chemotherapy drugs to kill cancer cells and slow tumor growth.
- Radiotherapy: Radiation is used to shrink tumors or prevent them from spreading.
- Immunotherapy: Modern treatments that use immune system boosters to fight cancer.
Prognosis and Patient Outlook
The prognosis for ovarian cancer patients depends on the cancer’s stage and how quickly it is diagnosed and treated. Early detection leads to more effective treatment and a higher survival rate. Newer treatments, including advanced chemotherapy and immunotherapy, can improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is one of the most dangerous and common cancers in women. However, if diagnosed early, its treatment has a higher chance of success. Awareness of symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options can aid in early detection and improve the quality of life for patients. Therefore, regular screenings and medical follow-ups are crucial for women over the age of 50.
Nutrition and Diet for Ovarian Cancer Patients
When it comes to nutrition and diet for ovarian cancer patients, choosing the right foods can help strengthen the immune system, improve general health, and facilitate the treatment process. Here are some important nutritional principles for ovarian cancer patients:
Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Antioxidants are natural substances that help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and may help facilitate cancer treatment. Some foods rich in antioxidants include:
- Fruits: Raspberries, strawberries, blueberries, cherries, apples, oranges, and grapefruits.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, cabbage, spinach, lettuce, carrots, and tomatoes.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds.
Diet with Healthy Fats
Healthy fats, such as unsaturated fats and omega-3s, are beneficial for boosting the immune system and improving overall health. Sources of healthy fats include:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, which are good sources of omega-3s.
- Avocados: Contain healthy fats, vitamins, and nutrients.
- Olive oil: An excellent source of healthy fats and antioxidants.
- Nuts and seeds: Such as almonds and walnuts, which also provide fiber and protein.
High-Fiber Diet
Fiber intake helps reduce inflammation, improve digestion, and control blood sugar levels. Foods rich in fiber include:
- Whole grains: Such as oats, brown rice, and whole-grain bread.
- Vegetables: Such as pumpkin, sweet potatoes, broccoli, and cauliflower.
- Fruits: Apples, pears, and plums.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
For ovarian cancer patients, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding excess weight is crucial. Consuming balanced and controlled healthy foods can help maintain weight and may prevent side effects from chemotherapy and hormone treatments.
Adequate Protein Intake
Protein is essential for repairing damaged tissues and strengthening the immune system. Patients undergoing chemotherapy or surgery may require more protein. Good sources of protein include:
- Chicken and fish: Lean sources of protein.
- Legumes: Such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans.
- Eggs and dairy products: Such as yogurt, cheese, and milk.
- Nuts and seeds: Such as almonds and pumpkin seeds.
Vitamins and Minerals
Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals is important for supporting the immune system and preventing nutritional deficiencies. Some vitamins and minerals that can help ovarian cancer patients include:
- Vitamin C: Supports the immune system and is found in fruits and vegetables like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and immune function, and can be obtained from sunlight or supplements.
- Folate: Found in leafy greens, legumes, and citrus fruits, and can help maintain cellular health.
Digestive Support
Chemotherapy and other treatments may affect the digestive system. Therefore, consuming foods that aid digestion can be beneficial. Some of these foods include:
- Ginger: Helps reduce nausea.
- Soups and broths: Liquid foods that are easier to digest.
- Bananas: A natural source of fiber that aids digestive health.
Hydration
Proper hydration is one of the key principles during cancer treatment. Patients should increase their fluid intake, especially if undergoing chemotherapy or other treatments that may lead to dehydration.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods and dietary habits may negatively affect the health of cancer patients. These foods include:
- Processed foods: Contain harmful chemicals and preservatives.
- Sugars and sweets: Excessive sugar intake can increase inflammation and weaken the immune system.
- Trans fats: Found in fried and processed foods, which may contribute to inflammation.
Final Notes
For ovarian cancer patients, proper nutrition and choosing healthy foods can help accelerate the treatment process, strengthen the immune system, and improve overall body health. Additionally, consulting with nutrition experts and doctors about the appropriate diet is highly recommended.
Psychology and the Role of Counseling in Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Ovarian cancer is a complex disease that not only affects the physical health of the patient but also significantly impacts their psychological and emotional state. The experience of diagnosis, treatment, and related care can cause substantial psychological stress. In this regard, psychological counseling is recognized as an essential part of the treatment process for ovarian cancer. Below is an exploration of the role of psychology and counseling in treating this disease:
- Coping with Stress and Anxiety
One of the first reactions for many patients after being diagnosed with ovarian cancer is intense stress and anxiety. Concerns about the future, treatment stages, and physical changes can significantly impact the patient’s quality of life. Psychological counseling can help the patient manage these anxieties and master relaxation techniques and stress management.
- Stress management: Psychologists can teach patients effective methods to reduce stress, such as breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness.
- Emotional support: Counselors can help patients identify and manage negative feelings like fear and worry, providing strategies to cope with these emotions.
- Increasing Psychological Resilience
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to face challenges and hardships and return to a previous or better state. Cancer treatment, especially in the early stages, can dramatically alter a person’s world. Psychological counseling can help strengthen the patient’s resilience and prepare them for the mental and physical challenges of the illness.
- Strengthening hope and motivation: Counselors can help patients find inner strength and hope, motivating them to continue treatment.
- Identifying support resources: Psychologists can guide patients to various support resources, such as support groups or close family members.
- Managing Depression and Mood Changes
Depression is a common psychological problem among cancer patients. Some patients, especially during chemotherapy or after surgery, may experience depression, lack of motivation, and low self-esteem. Psychological counseling can assist patients in coping with these issues and maintaining their quality of life.
- Coping techniques for depression: Psychologists can teach techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help patients alter negative thought and behavior patterns.
- Improving body image: Physical changes caused by cancer treatments can lead to body image issues and lower self-esteem. Counselors can help patients cope with these changes.
- Social Support and Family Communication
Another essential aspect of ovarian cancer treatment is social support. Patients need emotional support from their family, friends, and others during this sensitive time. Psychological counselors can help patients enhance their communication skills and establish positive and supportive relationships with others.
- Family education: Psychologists can offer families strategies for better understanding the psychological needs of the patient and how to provide adequate support.
- Support groups: Joining cancer support groups can help patients learn from others’ experiences and reduce feelings of loneliness.
- Strengthening a Sense of Control and Independence
A key psychological aspect of ovarian cancer treatment is helping patients feel in control. Cancer can induce feelings of helplessness and incapacity. Through counseling, patients can regain a greater sense of control over their lives.
- Setting short-term goals: Counselors can help patients set small, achievable goals throughout the treatment to enhance feelings of success and control.
- Encouraging self-care: Counselors can promote practices like proper nutrition, light exercise, and mental health care.
- Support in Facing Death and Accepting Reality
In cases where ovarian cancer has reached advanced stages, patients may face end-of-life issues. Psychological counseling in such cases can offer significant support for both the patient and their family.
- Acceptance process support: Counselors can help patients and families accept the reality of the disease, providing tools to cope with this crisis.
- Supporting difficult decisions: Counselors can assist patients in making informed decisions regarding treatment, quality of life, and end-of-life matters.
- Specific Psychological Treatment Techniques
Psychological treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), individual counseling, group counseling, and mindfulness-based therapies can effectively reduce anxiety, depression, and stress associated with ovarian cancer. These therapies help patients better understand their situation and manage negative emotions.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer treatment is certainly not limited to medical therapies; it requires a comprehensive approach that includes psychological support and counseling. Psychology and counseling can strengthen a patient’s resilience, reduce anxiety and depression, improve quality of life, and facilitate the treatment process. As a result, patients with psychological support can better cope with the physical and emotional challenges and achieve faster recovery.