Title: Breast Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Advanced Treatment Methods
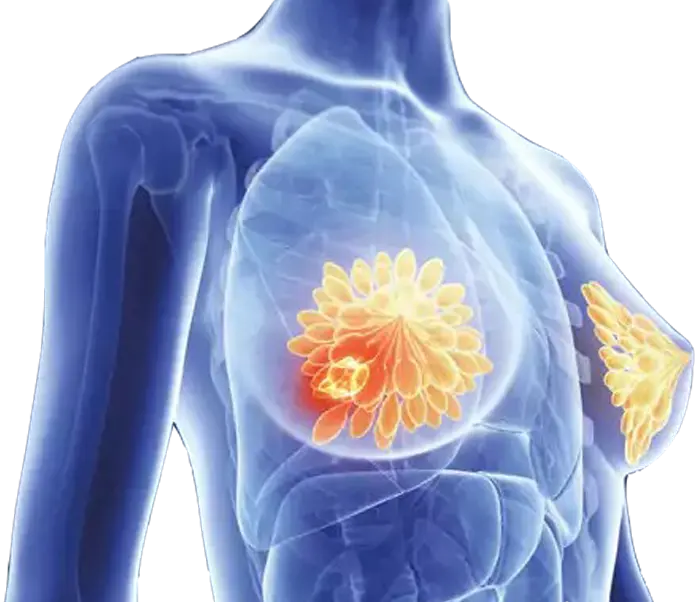
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women, occurring at any age but predominantly in women over 40. This disease develops when cells in the breast begin to grow abnormally, forming lumps. With advances in medical science, the methods for diagnosing and treating breast cancer have significantly improved. This article discusses the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatments available for breast cancer.
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
The symptoms of breast cancer may be painless in the early stages, but some common signs women should be aware of include:
- Unusual lumps in the breast or under the armpit
- Changes in the size, shape, or color of the breast
- Unusual bleeding or discharge from the nipple
- Pain or tenderness in the breast
- Difficulty in feeling the skin of the breast or the presence of skin lesions
It is important to inform a doctor about any abnormal changes in the breast to ensure early diagnosis and proper treatment.
Diagnostic Methods for Breast Cancer
To accurately diagnose breast cancer, doctors use several methods, including:
- Mammography: This is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to detect lumps or abnormal changes in the breast.
- Ultrasound: This method uses sound waves to create images from inside the breast and is particularly useful for evaluating unusual lumps.
- Biopsy: This involves taking a sample of breast tissue to be examined under a microscope to determine the type and characteristics of the cells.
- Breast MRI: This advanced imaging method is especially useful for evaluating breast lumps in women who are at higher risk.
Treatment Methods for Breast Cancer
Treatment for breast cancer varies depending on the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, and the patient’s overall condition. Common treatment methods include:
- Surgery: Surgery is one of the main treatments for breast cancer, where the cancerous lump or part of the breast is removed. Types of surgery include mastectomy (complete removal of the breast) and breast-conserving surgery (removal of only the cancerous lump).
- Chemotherapy: This treatment uses medications that target and prevent the multiplication of cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be administered before or after surgery.
- Radiation Therapy: This method uses radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is usually performed after surgery to prevent recurrence.
- Hormone Therapy: This treatment is used for hormone-sensitive breast cancers. Hormonal drugs reduce hormone levels in the body or block their effects on cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment enhances the body’s immune system to fight cancer. In some types of breast cancer, immunotherapy can be effective.
- Targeted Therapy: These treatments are designed for specific types of breast cancer that have unique characteristics. Targeted drugs specifically affect molecules in cancer cells to help destroy them.
Prevention and Post-Treatment Care
While breast cancer cannot be completely prevented, several methods can reduce the risk of developing it. Some of these methods include:
- A healthy diet with limited saturated fats and sugars.
- Regular exercise, which helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of breast cancer.
- Regular screenings and mammograms at appropriate ages for early detection.
- Psychological care: Psychological support for women with breast cancer is crucial, as cancer treatment can lead to emotional and mental challenges that need to be addressed.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women, but with early detection and appropriate treatment, it can be effectively managed. Advanced and specialized treatment methods, especially at top medical centers, can significantly increase the chances of recovery. Post-treatment care and prevention of disease recurrence also play a major role in improving the quality of life for patients. Additionally, being aware of the symptoms and consulting a doctor if there are any changes in the breast is a crucial step for successful treatment of this disease.