Corneal Transplant Surgery (Keratoplasty): Treating Corneal Diseases and Restoring Vision
Corneal transplant surgery, also known as keratoplasty, is an advanced and effective surgical method used to treat severe corneal diseases and injuries. This procedure can lead to significant improvement in the patient’s visual quality. It involves replacing a damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy donor cornea. Corneal transplantation is generally performed for patients who suffer from serious vision problems due to corneal diseases, trauma, or infections.
When Is a Corneal Transplant Needed?
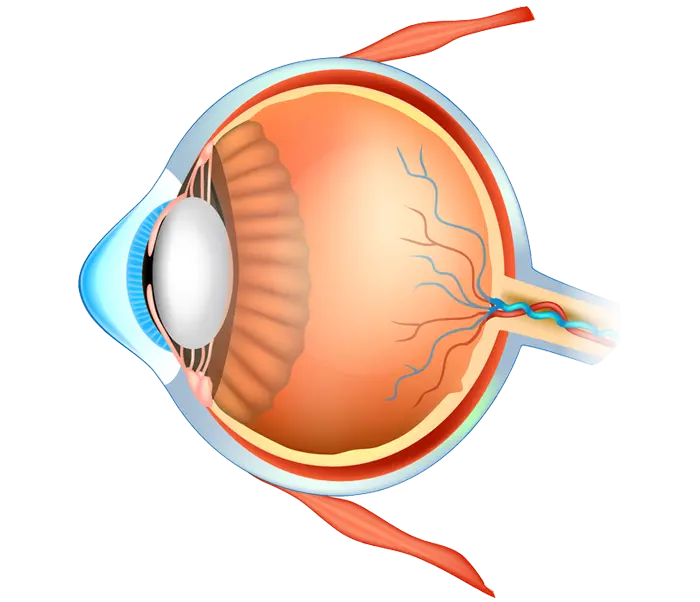
The cornea is the clear, front layer of the eye that plays a crucial role in focusing light and ensuring clear vision. When the cornea is damaged by disease, injury, or infection, it can lead to serious visual impairment or even blindness. A corneal transplant may be recommended in the following cases:
- Corneal Diseases:
• Keratoconus: A condition in which the cornea becomes thin and cone-shaped, leading to severe blurred vision.
• Corneal Degeneration: Progressive damage to the corneal structure over time.
• Corneal atrophy or scarring: Caused by prior diseases or surgical procedures. - Physical or Chemical Trauma:
• Injuries from accidents or burns that damage the cornea.
• Eye trauma resulting in corneal rupture or deformation. - Chronic Infections and Inflammation:
• Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, which may result in scarring and vision loss.
• Damage caused by herpes simplex infections leading to corneal scarring. - Complications from Previous Transplants:
• Patients who have previously undergone corneal transplants but experienced graft rejection or complications.
The Corneal Transplant Procedure
Corneal transplantation is a complex surgery that requires high precision and expertise. It is typically performed in a hospital surgical setting using advanced equipment. The surgical process includes the following stages:
- Preoperative Preparation and Evaluation:
• Comprehensive eye examination: Prior to surgery, the patient undergoes detailed evaluations including corneal thickness measurement, optic nerve assessment, and general eye health checks.
• Tests and screenings: Reviewing medical history, conducting blood tests, and ensuring no active infections are essential steps before surgery. - Types of Corneal Transplants:
Corneal transplants are performed using two primary techniques:
• Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK): The full thickness of the damaged cornea is removed and replaced entirely with a healthy donor cornea.
• Lamellar Keratoplasty (LK): Only the affected layers of the cornea are removed. This method is often used for conditions such as keratoconus. - Surgical Procedure:
• Anesthesia: The surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia or sedation, ensuring the patient feels no pain.
• Removal of the damaged cornea: The surgeon carefully excises the diseased corneal tissue using precise instruments.
• Implantation of the donor cornea: The new cornea is meticulously positioned and sutured into place using fine stitches. - Postoperative Recovery and Care:
• Rest and eye protection: Patients are typically advised to wear an eye shield and avoid touching the eye.
• Medications and eye drops: Anti-inflammatory and antibiotic eye drops are prescribed to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
• Follow-up visits: Regular checkups are necessary to monitor the healing of the graft and detect any signs of rejection.
Benefits and Challenges of Corneal Transplant Surgery
Benefits:
• Vision restoration: Most patients experience significant visual improvement following the surgery.
• Enhanced quality of life: Restored vision allows patients to return to daily activities.
• Generally low-risk procedure: With proper care, corneal transplantation is highly successful.
Challenges and Potential Complications:
• Graft rejection: A primary concern, which may require additional interventions or surgery.
• Infections: Postoperative infections can pose serious risks and may lead to permanent damage.
• Prolonged recovery: Full visual recovery may take several months.
• Fluctuating vision: Temporary blurriness may occur until the new cornea fully stabilizes.
Conclusion
Corneal transplant surgery is a proven and successful method for treating severe corneal disorders and injuries. It can significantly restore vision and improve patients’ quality of life. The procedure requires the expertise of skilled ophthalmic surgeons and proper postoperative care to ensure optimal outcomes.
If you or someone close to you is affected by corneal disease, consulting with an ophthalmologist and undergoing a thorough evaluation is a vital first step. Thanks to modern medical advancements and access to cutting-edge technologies, corneal transplantation has become a reliable and effective treatment—offering hope of restored vision to those suffering from corneal conditions.
The Role of Nutrition in Corneal Transplant Recovery and Eye Health
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in the recovery process following corneal transplant surgery. As a complementary factor to medical treatment, a well-balanced diet can accelerate healing, prevent postoperative complications, and support overall eye health. Corneal transplantation is a sensitive and complex procedure, and the body requires sufficient resources to repair tissues and maintain a strong immune system. Below, we explore the most important nutrients, vitamins, and dietary elements that contribute to a successful recovery after corneal transplant surgery:
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants—particularly Vitamin C and Vitamin E—are crucial for protecting the eyes and supporting the repair of damaged corneal tissue. These vitamins combat free radicals that can harm cells, reduce inflammation, and help preserve corneal integrity.
- Vitamin C aids in the production of collagen, which is essential for tissue regeneration. Excellent sources include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, kiwis), bell peppers, strawberries, and vegetables such as broccoli.
- Vitamin E protects cells and tissues from inflammation-induced damage. Good sources include plant-based oils (like olive oil), nuts, and seeds (such as almonds, hazelnuts, and sunflower seeds).
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines, are known for their strong anti-inflammatory properties. These healthy fats help alleviate inflammation in affected areas, support corneal tissue healing, and reduce the risk of postoperative infections.
- Plant-based Omega-3 sources include flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, all of which are excellent additions to a post-surgical diet.
- Zinc-Rich Foods
Zinc is an essential mineral for tissue repair and maintaining a healthy immune system. It accelerates the healing process after corneal transplant surgery and helps defend against potential infections.
- Rich dietary sources of zinc include red meat, poultry, seafood (such as oysters and fish), legumes (like beans and lentils), eggs, and nuts (including pistachios and almonds).
- Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in overall health and in managing postoperative inflammation. It contributes to bone health and immune system function—both critical for recovery. Its immune-supporting effects are especially beneficial for preventing infections.
- Sources of Vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon and tuna), eggs, and dairy products fortified with vitamin D. Additionally, regular exposure to sunlight can help stimulate natural vitamin D production in the body.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Reducing inflammation is a top priority after corneal transplant surgery. Certain natural foods have anti-inflammatory properties that can assist in a faster and smoother recovery.
- Turmeric (containing curcumin), ginger, and garlic are among the most effective anti-inflammatory foods.
- Turmeric and ginger not only reduce inflammation but also have antimicrobial properties, helping prevent postoperative infections.
- Garlic acts as a natural antibiotic and can strengthen the immune system while decreasing inflammation.
- Proper Hydration
Adequate hydration is one of the most important factors for a swift recovery after corneal transplantation. Fluids aid in tissue repair and help prevent dry eyes and other related issues. Suitable sources include water, natural fruit juices (without added sugar), and broths.
- It is advisable to avoid caffeine and alcoholic beverages, as these can contribute to dehydration and dry eyes.
- Dietary Fiber to Prevent Constipation
Constipation is a common issue after surgery, especially when physical activity is reduced. A diet rich in fiber helps maintain digestive health and prevent discomfort during recovery.
- High-fiber foods include leafy green vegetables, fruits, legumes (such as beans and lentils), and whole grains.
- Avoiding Processed Foods and Unhealthy Fats
After corneal transplant surgery, it is essential to maintain a healthy, natural diet. Processed foods, trans fats, and added sugars can slow the healing process and increase inflammation. Avoiding these is crucial for a successful recovery.
- Unhealthy fats—particularly trans fats found in fast foods and processed snacks—should be minimized to reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
A nutritious and balanced diet following corneal transplant surgery can significantly enhance recovery and improve clinical outcomes. Consuming foods rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids, along with proper hydration, can accelerate healing, reduce inflammation, and help prevent infections. Maintaining a healthy, nutrient-dense diet is particularly critical during the post-operative period to ensure patients achieve full recovery and benefit from restored vision.