Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR): A Minimally Invasive and Effective Treatment for Tear Duct Obstruction
Introduction
Tear duct obstruction is a common condition affecting individuals of various ages, typically caused by chronic infections, inflammation, or structural abnormalities within the lacrimal drainage system. This condition often leads to excessive tearing (epiphora), cosmetic concerns, and functional discomfort. One of the most advanced and effective treatments available for this condition is Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) — a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed using endoscopic technology.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the DCR procedure, its steps, benefits, and key reasons why it is increasingly preferred by both patients and specialists.
Why Choose Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)?
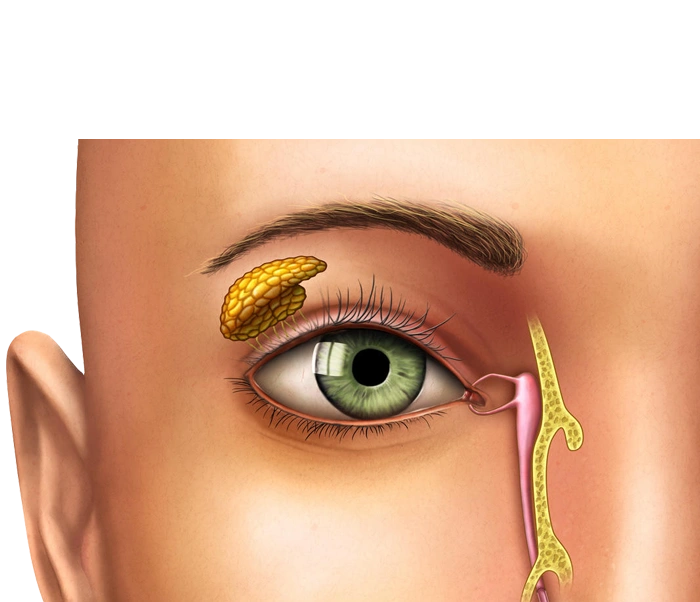
The human tear drainage system is designed to carry tears from the eyes into the nasal cavity via the nasolacrimal duct. Obstruction in this duct can occur due to chronic infections, tumors, trauma, or congenital anomalies. As a result, tears accumulate in the eye, causing discomfort, discharge, and inflammation.
While various treatments exist, Endoscopic DCR is considered one of the most effective and least invasive options, especially for patients with chronic tear duct blockage who have not responded to other therapies.
What Is Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)?
Endoscopic DCR is a surgical procedure that uses an endoscope to create a new pathway for tear drainage between the eye and the nasal cavity — without any large skin incisions. Using a thin endoscopic tube equipped with a camera, the surgeon accesses the nasal cavity and removes the bone wall between the lacrimal sac and the nasal passage, forming a direct route for tears to drain.
Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Anesthesia: The surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition.
- Endoscopic Access: The surgeon inserts the endoscope — a thin tube with a light and camera — into the nasal passage to locate the blockage.
- Creating an Opening: A small hole is made in the thin bone wall between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity.
- Establishing the New Drainage Pathway: A new duct is formed to allow tears to drain from the eye directly into the nose.
- Stenting and Healing: In some cases, a temporary stent or tube is placed in the new duct to maintain patency during the healing process.
Benefits of Endoscopic DCR
- Minimally Invasive with No External Scars:
This technique avoids any external facial incisions, reducing postoperative discomfort and leaving no visible scars. - Quick Recovery and Return to Daily Life:
Due to its minimally invasive nature, most patients experience a short recovery period and can return to normal activities shortly after the procedure. - High Precision and Effectiveness:
The use of modern endoscopic equipment enables precise localization and treatment of the obstruction, significantly improving success rates. - Lower Risk of Complications:
The internal approach reduces the risk of bleeding, infection, and scarring compared to traditional surgical methods. - Short Hospital Stay:
Most patients can be discharged shortly after the surgery, with no need for prolonged hospitalization.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Endoscopic DCR?
• Patients with Chronic Tear Duct Obstruction:
This procedure is ideal for individuals who have persistent tear duct blockage and have not achieved relief from non-surgical treatments.
• Failed Non-Surgical Treatments:
When medications or alternative methods are ineffective, Endoscopic DCR provides a reliable surgical solution.
• Suitable Across All Age Groups:
The surgery can be safely performed on patients of various ages, including those with underlying health conditions or anatomical challenges.
Postoperative Care Guidelines
To ensure optimal healing and prevent complications, patients should follow these care recommendations:
- Use of Prescribed Medications:
Anti-inflammatory and antibiotic medications may be prescribed to reduce swelling and prevent infection. - Avoid Eye Pressure:
Patients should avoid applying pressure to the eyes to protect the newly created duct. - Scheduled Follow-Up Visits:
Regular postoperative visits help the physician monitor recovery and address any potential issues. - Stent Maintenance (If Applicable):
If a temporary stent is placed, it should remain in position for the recommended duration to support proper healing.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a highly advanced and effective surgical method for managing tear duct obstruction. With its minimally invasive approach, high precision, short recovery time, and reduced risk of complications, DCR has become a preferred treatment for both patients and eye specialists.
If you or someone you know suffers from chronic tearing or tear duct blockage and is seeking a safe and effective solution, Endoscopic DCR may be the ideal option.
For expert consultation and appointment scheduling with trusted specialists, feel free to reach out to accredited medical centers recommended by CCKAAM.